The chronicles of history remind us of the grandiose rise and inevitable fall of ancient empires, whose legacies continue to influence modern civilization in profound ways. The story of these empires—from the enduring might of Rome to the scholarly zenith of the Han Dynasty—provides us with a lens through which to view our contemporary world. Understanding these ancient marvels isn’t merely an academic pursuit; it is crucial in uncovering timeless truths about governance, culture, warfare, and economics that are as relevant today as they were millennia ago.
By examining the pathways to power and the causes of decay, we lay bare the immutable principles that govern human societies. This intricate tapestry of history offers invaluable lessons; today’s global leaders and policymakers constantly turn back the pages of time to harness insights that can be applied in steering modern statecraft and international relations. This article delves deeply into these themes, examining recent scholarly updates on the topic, with an emphasis on the elucidation of lessons learned from the historical trajectory of ancient empires.
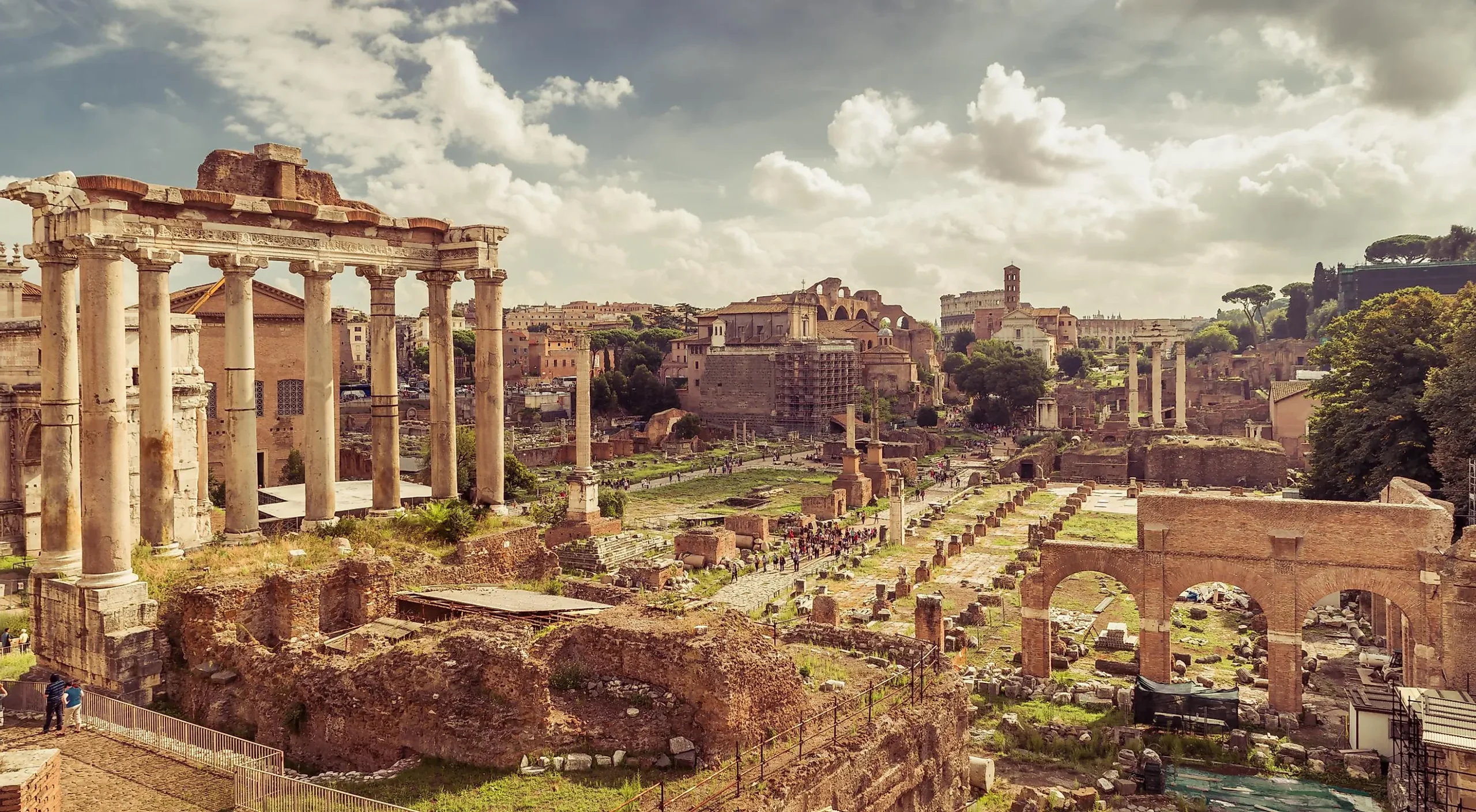

The Roman Empire: Governance and Military Prowess
The Roman Empire’s extensive duration and the breadth of its territories make it one of the most studied and iconic empires in history. It offers rich lessons in governance and military strategizing. Recent archaeological discoveries and modern historiographical approaches have provided exciting updates about the life and times of Rome, enhancing our understanding of its intricacies.
Past studies attributed Rome’s expansionist success to its formidable military structure. Yet, recent scholarship underscores the complexity of its governance systems as an equally vital component. From an intricate Senate to a well-designed bureaucratic system, Rome’s internal governance mechanisms are seen as innovative templates for balancing power among various administrative facets. This merits consideration in today’s discussions on decentralization and federalism. Parallels can be drawn particularly with federal models in modern nations where state authority coexists with centralized power.
Moreover, the Roman military might was underpinned by strategic logistics and pioneering engineering feats, such as the construction of roads and aqueducts that not only facilitated troop movement but boosted the economy, intertwining military and civil engineering. The systematic training and discipline of Roman legions lay the Yowestogel groundwork for contemporary military doctrines. However, it was not merely brute force that kept the empire in unison during its zenith; it was also Rome’s ability to integrate conquered peoples, exemplifying inclusivity and adaptability.
Recent studies suggest the empire’s undoing came from within—decadence, political corruption, and over-reliance on mercenary troops sapped the state’s robustness, leading to decline. This has prompted modern-day discourse on the sustainability of power and the risks of internal decay. Today’s political arenas can draw from these lessons, understanding that the durability of institutions hinges upon ethical governance and citizen integration rather than expansionist aspirations alone.
Insights from Modern Advancements
Technological advancements in archaeological methods have unveiled previously unknown facets of Roman urban planning and socio-political structures. Advanced imaging techniques have uncovered lost cities under modern landscapes, providing insights into how cities were managed sustainably. This is invaluable in facing today’s urbanization challenges, pushing for cities that balance growth with habitation comfort and infrastructure robustness.
The Han Dynasty: Culture and Economy
The Han Dynasty, often juxtaposed with the Roman Empire due to its simultaneous existence, echoed a different tale of power consolidated through cultural opulence and economic foresight. Recent discoveries in ancient texts and artefacts have deepened our understanding of how the Han Dynasty set cultural precedents that defined Chinese identity.
The Han era’s emphasis on Confucian ideals catalyzed a cultural and educational framework that underpinned its governance model. This civil service system was remarkably progressive for its time, promoting meritocracy based on educational attainment. The ‘Mandate of Heaven’ concept implemented during Han rule ensured that the emperor remained a figurehead as long as he ruled justly—a precursor to the modern-day constitutional moral expectations of leaders.
From an economic perspective, the Silk Road established during the Han period laid the foundations for transcontinental trade. This ancient trade network highlights global interconnectedness long before contemporary globalization and demonstrates the nuances of cultural exchange and economic integration. Current global markets echo the Han Dynasty’s trade innovations, with emphasis placed on how historical economic infrastructures evolved and flourished by adapting to new trading environments and political climates.
However, the Han Dynasty’s fall was precipitated by widening economic disparities and bureaucratic corruption—a tale as pertinent today as then. This reiterates the idea that sustainable economic policies must address both growth and equality, with modern financial institutions learning from these missteps.
Cultural Resonance in Today’s World
Recent academic endeavors have traced the influence of Han culture in diverse realms ranging from literature to architectural design. Studies show that the Han’s prioritization of certain cultural facets promotes social cohesion, a principles connoted in contemporary identity politics and cultural policymaking. As global societies face questions of cultural authenticity and integration, the Han’s strategic use of culture serves as a beacon.
The Persian Empire: Tolerance and Administration
Long before Roman and Chinese empires dominated their respective territories, the Persian Empire under Cyrus the Great had set benchmarks in administration and cultural tolerance still revered today. Recent archaeological studies, particularly in Pasargadae, enhance our appreciation of Persian innovations in empire building.
The Persian administrative model saw the division of its vast empire into satrapies, each governed by a satrap, ensuring decentralized yet coherent control. This method of governance has parallels to modern administrative divisions, advocating for regional autonomy to manage local affairs. Balancing local governance within a central framework is a principle observed by modern federal systems worldwide.
Cyrus the Great’s policies of tolerance, as inscribed in the Cyrus Cylinder, are recognized as early forms of human rights charters. These principles of tolerance and freedom of worship resonate fiercely in today’s discourse on human rights, especially in multicultural nations striving for harmony amid diversity.
However, while the Persian Empire excelled in administration and cultural inclusivity, its downfall was accelerated by overexpansive conquests and inability to adapt strategically. This serves as an admonition to the potential pitfalls overextension breeds, pertinent to superpowers’ contemporary engagements.
Implications for Modern Governance
New statistical data evaluating the Persian administrative model identifies effective bureaucratic practices still relevant. These include data-driven decisions and resource management aimed at ensuring equitable resource distribution, applicable today in managing multinational states and corporate entities.
The Maurya Empire: Rule and Philosophy
The Maurya Empire, notably under Ashoka, epitomized the merging of political might with philosophical introspection. The edicts of Ashoka are a testament to early ethical governance models that contemporary political theorists and practitioners aspire to emulate. Recent interpretations of these edicts suggest deeper layers of administration, preventive justice, and social welfare.
Under Mauryan rule, a centralized bureaucracy and an advanced taxation system embodied efficiency. Their strategic military conquests, followed by an adoption of pacifism and Buddhism, delineates a narrative of power tempered by philosophical awakening. This transformation offers lessons in ethical leadership—adopting changes consonant with ethical values even at the peak of political dominance.
Recent discoveries at historical sites, enabled by laser scanning technologies, reveal intricate city planning that underscores the synergy between administration and economy prevalent in the Mauryan reign. Moreover, the emphasis Ashoka laid on infrastructure, public health, and education underscores the importance of a welfare state—a concept increasingly debated in modern politics.
Philosophical Perspectives for Today
Ashoka’s embrace of Buddhism and promulgation of ethical governance have contemporary relevance as societies stress moral leadership. Initiatives inspired by these ancient philosophies are being integrated into leadership development programs, impacting institutional cultures and leadership paradigms worldwide.
Conclusion
The rise and fall of ancient empires present a complex interplay of power, ethics, culture, and economy, with timeless lessons for today’s global landscape. As recent scholarly updates provide fresh insights into their successful models and pitfalls, these narratives compel modern societies to introspect on their trajectories. The durability of institutions, the balance between growth and governance, and the ethics of leadership underscore the core takeaways from these ancient empires.
The art of maintaining power, as documented through history, lies in adapting to evolving circumstances and ensuring that the human core of governance remains robust yet flexible. In an interconnected and rapidly changing world, these historical narratives offer both warnings and guidance as humanity steps forward on the broad stage of modern statecraft and international affairs. With the past as our guide, the potential to forge a harmonious and progressive future is promising. If you like reading this article then visit https://terredesurf.com/ to find more article like this.










